Spring:Datenbanken: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) (Die Seite wurde neu angelegt: „== Set Up or Tear Down Outside of a Transaction == You can annotate a <code>public void</code> method with <code>@BeforeTransaction</code> or <code>@AfterTrans…“) |
Admin (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
== Set Up or Tear Down Outside of a Transaction == | == Set Up or Tear Down Outside of a Transaction == | ||
You can annotate a <code>public void</code> method with <code>@BeforeTransaction</code> or <code>@AfterTransaction</code>. This indicates to Spring that this method should be run before or after a test method is run within a transaction. | You can annotate a <code>public void</code> method with <code>@BeforeTransaction</code> or <code>@AfterTransaction</code>. This indicates to Spring that this method should be run before or after a test method is run within a transaction. | ||
=====CGlib & JDK Proxies - @Transactional under the covers===== | |||
Spring cannot really rewrite your Java class, like I did above, to insert the connection code (unless you are using advanced techniques like bytecode weaving, but we are ignoring that for now). | |||
Your registerUser() method really just calls userDao.save(user), there’s no way to change that on the fly. | |||
But Spring has an advantage. At its core, it is an IoC container. It instantiates a UserService for you and makes sure to autowire that UserService into any other bean that needs a UserService. | |||
Now whenever you are using @Transactional on a bean, Spring uses a tiny trick. It does not just instantiate a UserService, but also a transactional ''proxy'' of that UserService. | |||
It does that through a method called ''proxy-through-subclassing'' with the help of the [https://github.com/cglib/cglib Cglib library]. There are also other ways to construct proxies (like [https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/reflection/proxy.html Dynamic JDK proxies]), but let’s leave it at that for the moment. | |||
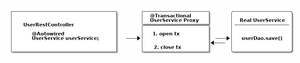
Let’s see proxies in action in this picture: | |||
[[Datei:Spring proxy transaction.png|mini]] | |||
Version vom 23. November 2021, 10:30 Uhr
Set Up or Tear Down Outside of a Transaction
You can annotate a public void method with @BeforeTransaction or @AfterTransaction. This indicates to Spring that this method should be run before or after a test method is run within a transaction.
CGlib & JDK Proxies - @Transactional under the covers
Spring cannot really rewrite your Java class, like I did above, to insert the connection code (unless you are using advanced techniques like bytecode weaving, but we are ignoring that for now).
Your registerUser() method really just calls userDao.save(user), there’s no way to change that on the fly.
But Spring has an advantage. At its core, it is an IoC container. It instantiates a UserService for you and makes sure to autowire that UserService into any other bean that needs a UserService.
Now whenever you are using @Transactional on a bean, Spring uses a tiny trick. It does not just instantiate a UserService, but also a transactional proxy of that UserService.
It does that through a method called proxy-through-subclassing with the help of the Cglib library. There are also other ways to construct proxies (like Dynamic JDK proxies), but let’s leave it at that for the moment.
Let’s see proxies in action in this picture: